NClex questions on acute kidney injury (AKI) demand a comprehensive understanding of this critical condition. AKI, a sudden decline in kidney function, poses significant challenges for healthcare professionals, necessitating prompt recognition and effective management.
This guide delves into the pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, and management strategies of AKI, equipping nurses with the knowledge and skills to provide optimal care for patients facing this condition.
Overview of Acute Kidney Injury (AKI)
AKI is a rapid decline in kidney function over a few hours or days. It can be caused by various factors, including ischemia, toxins, and infections. AKI can lead to a buildup of waste products in the blood, electrolyte imbalances, and fluid overload.
Causes of AKI
- Prerenal causes: reduced blood flow to the kidneys, such as in dehydration, hypotension, or sepsis
- Renal causes: direct damage to the kidneys, such as in glomerulonephritis, pyelonephritis, or acute tubular necrosis
- Postrenal causes: obstruction of the urinary tract, such as in kidney stones, prostate enlargement, or tumors
Clinical Manifestations of AKI
AKI can present with various signs and symptoms, depending on the severity of the injury. Early recognition and diagnosis are crucial to prevent complications and improve outcomes.
Signs and Symptoms, Nclex questions on acute kidney injury
- Decreased urine output (oliguria or anuria)
- Edema (swelling) in the face, hands, feet, and legs
- Fatigue
- Nausea and vomiting
- Confusion or disorientation
- Shortness of breath
Management of AKI: Nclex Questions On Acute Kidney Injury
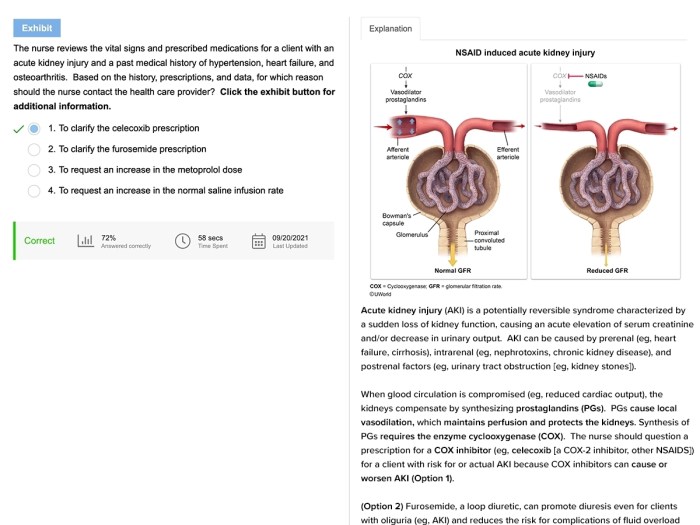
AKI management focuses on addressing the underlying cause, supporting kidney function, and preventing complications.
Principles of Management
- Identify and treat the underlying cause
- Maintain fluid and electrolyte balance
- Provide nutritional support
- Monitor for complications and provide appropriate treatment
Fluid and Electrolyte Management
AKI patients may require fluid restriction or diuretics to manage fluid overload. Electrolyte imbalances, such as hyperkalemia or hypocalcemia, should be corrected promptly.
Dialysis
Dialysis is a procedure that removes waste products and excess fluid from the blood when the kidneys are unable to function adequately. It can be performed using hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis.
Nursing Care for Patients with AKI
Nurses play a vital role in caring for patients with AKI.
Nursing Interventions
- Monitor vital signs and fluid balance
- Administer medications as prescribed
- Provide nutritional support
- Educate patients and families about AKI and its management
- Prevent and manage complications, such as infection and electrolyte imbalances
Helpful Answers
What are the common causes of AKI?
AKI can result from various factors, including sepsis, dehydration, nephrotoxins, and obstructive uropathy.
How is AKI diagnosed?
AKI is diagnosed based on a combination of blood tests (creatinine and urine output) and physical examination findings.
What are the principles of AKI management?
AKI management focuses on identifying and addressing the underlying cause, maintaining fluid and electrolyte balance, and providing renal replacement therapy if necessary.
What is the role of nurses in caring for patients with AKI?
Nurses play a crucial role in monitoring vital signs, assessing fluid status, administering medications, and providing patient education and support.