Article 445 contains installation and other requirements for generators, providing a comprehensive guide for the safe and effective use of these essential power sources. This article establishes the standards for installing, operating, and maintaining generators, ensuring their reliable performance and minimizing potential hazards.
From understanding the different types of generators to following proper safety precautions, Article 445 covers a wide range of topics crucial for generator users. Whether you’re a homeowner, business owner, or professional electrician, this article provides valuable insights and practical guidance to ensure the safe and efficient operation of your generator.
Generator Installation and Requirements
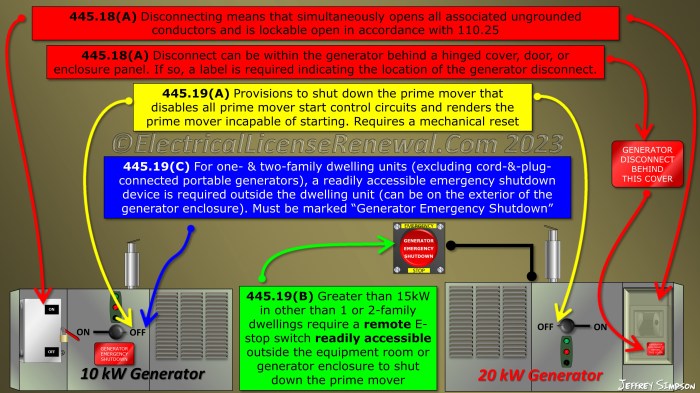
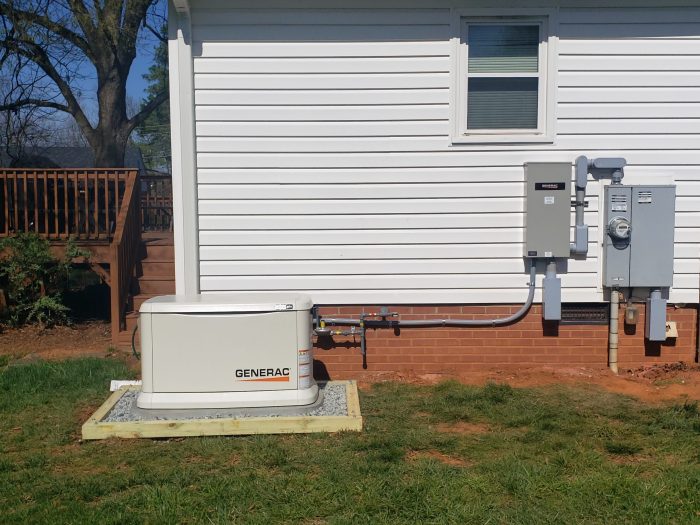
Generators provide a reliable source of electricity during power outages, ensuring essential operations and comfort. Proper installation and maintenance are crucial for safe and efficient operation. This article Artikels the installation requirements, generator types, safety precautions, maintenance, and sizing considerations for generators.
Question Bank: Article 445 Contains Installation And Other Requirements For Generators
What are the minimum hardware requirements for installing a generator?
The minimum hardware requirements vary depending on the type and size of the generator. However, generally, a generator requires a stable platform, proper ventilation, and adequate electrical wiring.
What are the different types of generators available?
There are three main types of generators: portable, standby, and inverter generators. Portable generators are designed for temporary use and can be easily transported. Standby generators are permanently installed and provide backup power during outages. Inverter generators produce clean power and are ideal for sensitive electronic devices.
What are the potential hazards associated with using generators?
Generators can pose several potential hazards, including carbon monoxide poisoning, electrical shock, and fire. It is crucial to follow proper safety precautions, such as operating generators in well-ventilated areas, grounding them properly, and using them according to the manufacturer’s instructions.

