Epithelia, the versatile guardians of our bodies, line our organs and cavities, forming a crucial interface between the internal and external environments. In this guide, we embark on a journey to identify the epithelium indicated by the arrows, unraveling the secrets of these specialized tissues and their pivotal roles in health and disease.
Through microscopic images, we will explore the diverse types of epithelia, from the delicate simplicity of simple epithelium to the robust protection of stratified epithelium. We will delve into the techniques that enable us to distinguish between these tissues, including staining, immunohistochemistry, and electron microscopy.
Introduction
Epithelium is a type of tissue that lines the surfaces of organs and cavities in the body. It serves as a barrier between the internal environment and the external environment, and it also regulates the exchange of substances between the two environments.
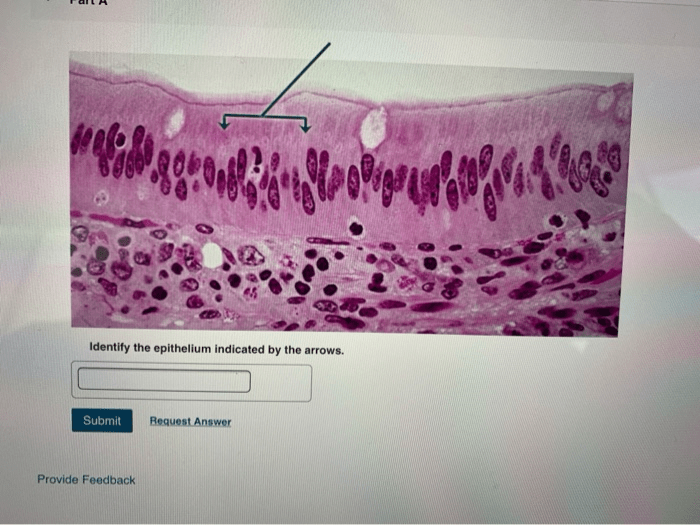
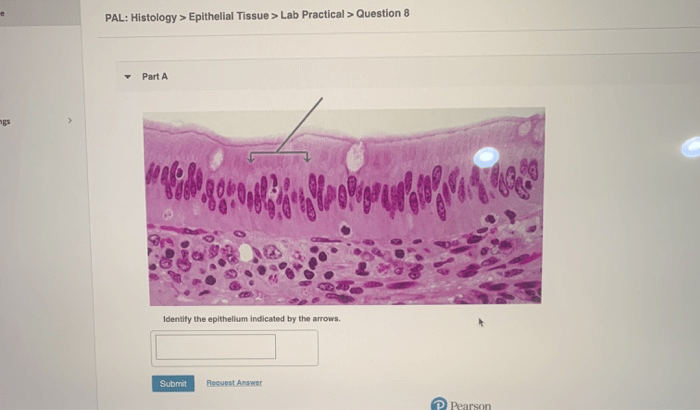
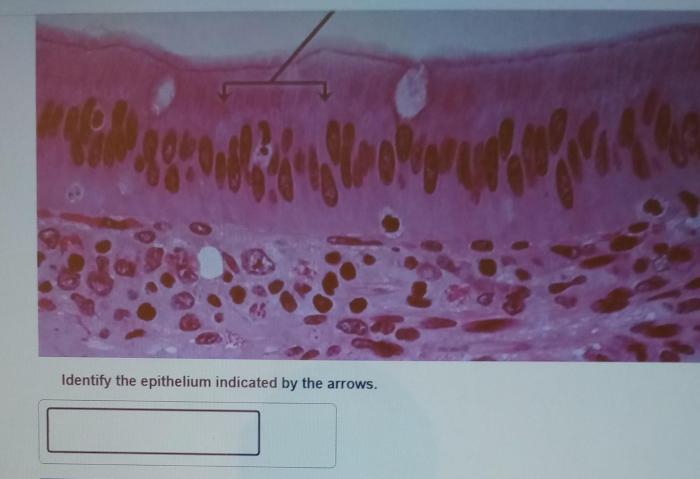
Epithelial tissues are classified into different types based on their structure and function. The arrows in microscopic images can help identify specific epithelial tissues. For example, simple epithelium is a single layer of cells, while stratified epithelium is multiple layers of cells.
Methods of Identifying Epithelium
Epithelial cells can be visualized using different staining techniques. Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining is a common technique that stains nuclei blue and cytoplasm pink. Immunohistochemistry is another technique that uses antibodies to stain specific proteins in epithelial cells. This technique can help distinguish between different epithelial types.
Electron microscopy is a technique that can be used to examine the ultrastructure of epithelial cells. This technique can provide detailed information about the structure of the cell membrane, cytoplasm, and nucleus.
Types of Epithelium
| Type of Epithelium | Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Simple epithelium | Single layer of cells |
| Stratified epithelium | Multiple layers of cells |
| Pseudostratified epithelium | Single layer of cells that appear to be stratified |
| Transitional epithelium | Cells that change shape depending on the state of the organ |
Location and Function of Epithelium
Epithelium is found in various locations in the body, including the skin, digestive system, respiratory system, and urinary system. The specific function of the epithelium depends on its location.
For example, the epithelium in the skin provides a barrier against pathogens and helps to regulate body temperature. The epithelium in the digestive system helps to absorb nutrients and protect against harmful substances. The epithelium in the respiratory system helps to exchange gases between the blood and the air.
Clinical Significance of Epithelium: Identify The Epithelium Indicated By The Arrows
Epithelium plays an important role in maintaining homeostasis and protecting against pathogens. Changes in epithelial structure and function can lead to diseases such as cancer and infections.
For example, cancer can occur when epithelial cells begin to grow uncontrollably. Infections can occur when pathogens breach the epithelial barrier and enter the body.
FAQ Section
What is the significance of arrows in identifying epithelium?
Arrows in microscopic images serve as visual cues, guiding our attention to specific epithelial regions. By carefully examining the morphology and arrangement of cells indicated by the arrows, we can make informed deductions about the type of epithelium present.
How does staining aid in epithelium identification?
Staining techniques selectively highlight different cellular components, allowing us to visualize and differentiate between various epithelial types. For instance, hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining is commonly used to distinguish between the nucleus and cytoplasm, providing valuable clues about cell structure and organization.
What is the role of immunohistochemistry in epithelium identification?
Immunohistochemistry employs antibodies to target and visualize specific proteins within epithelial cells. This technique enables us to identify and characterize different epithelial subtypes based on their unique protein expression profiles.