Embark on an enlightening journey into the realm of motion with our comprehensive Section 11.2 Speed and Velocity Answer Key. This meticulously crafted resource unravels the intricacies of speed and velocity, empowering you with a profound understanding of these fundamental concepts.
Delving into the heart of the matter, we will meticulously define speed and velocity, illuminating their subtle distinctions. Through a series of illustrative examples and precise calculations, we will unravel the formulas that govern these quantities, empowering you to navigate the complexities of motion with ease.
Speed and Velocity: Section 11.2 Speed And Velocity Answer Key
Speed and velocity are two fundamental concepts in physics that describe the motion of objects. Speed is the rate at which an object changes its position, while velocity is the rate at which an object changes its position in a specific direction.
Define Speed and Velocity, Section 11.2 speed and velocity answer key
Speed is a scalar quantity that measures the distance traveled by an object per unit time. It is typically measured in meters per second (m/s) or kilometers per hour (km/h). Velocity, on the other hand, is a vector quantity that measures the displacement of an object per unit time in a specific direction.
It is typically measured in meters per second (m/s) or kilometers per hour (km/h) in a specified direction.
Calculate Speed and Velocity
The formulas used to calculate speed and velocity are as follows:
- Speed = Distance / Time
- Velocity = Displacement / Time
Displacement is the change in position of an object in a specific direction. It is calculated by subtracting the initial position from the final position.
Applications of Speed and Velocity
Speed and velocity are used in everyday life in a variety of applications, such as:
- Physics: Speed and velocity are used to describe the motion of objects in motion.
- Engineering: Speed and velocity are used to design and control machines and vehicles.
- Sports: Speed and velocity are used to measure the performance of athletes.
Relate Speed and Velocity to Other Physical Quantities
Speed and velocity are related to other physical quantities, such as distance, time, and acceleration. The following table illustrates these relationships:
| Quantity | Formula |
|---|---|
| Distance | Speed x Time |
| Time | Distance / Speed |
| Acceleration | Change in Velocity / Time |
Advanced Concepts in Speed and Velocity
There are a number of advanced concepts related to speed and velocity, such as:
- Relative velocity: The velocity of an object relative to another object.
- Average velocity: The average speed of an object over a period of time.
- Instantaneous velocity: The velocity of an object at a specific instant in time.
These concepts are used to describe more complex motion, such as the motion of objects in circular paths or the motion of objects under the influence of forces.
Question & Answer Hub
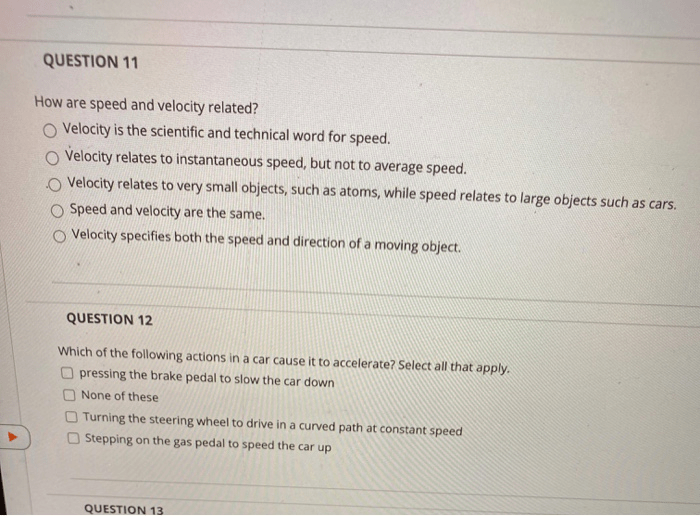
What is the primary distinction between speed and velocity?
Speed measures the rate at which an object traverses a distance, while velocity encompasses both speed and direction.
Can you provide an example to illustrate the difference between speed and velocity?
Consider a car traveling at 60 miles per hour. Its speed is 60 mph, but its velocity is 60 mph north if it is traveling in a northerly direction.
How is speed calculated?
Speed is calculated by dividing the distance traveled by the time taken to cover that distance: Speed = Distance / Time.