Welcome to the AP Bio Cell Communication Quiz, your ultimate guide to the fascinating world of cell-to-cell communication. Get ready to delve into the intricacies of cell signaling, explore the role of communication in health and disease, and discover the cutting-edge applications of cell communication research.
From the basics of cell communication methods to the complexities of cell signaling pathways, this quiz will test your knowledge and deepen your understanding of this essential biological process.
Cell Communication Methods
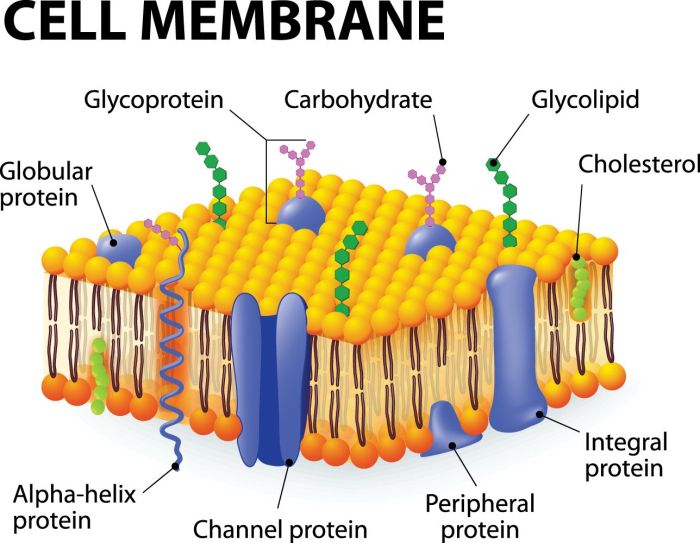
Cell communication is the process by which cells transmit information to each other. This process is essential for coordinating the activities of cells within an organism and for maintaining homeostasis. There are three main types of cell communication: autocrine signaling, paracrine signaling, and endocrine signaling.
Autocrine Signaling
Autocrine signaling occurs when a cell secretes a signaling molecule that binds to receptors on the same cell. This type of signaling is often used to regulate cell growth and differentiation. For example, the hormone erythropoietin is secreted by kidney cells in response to low oxygen levels.
Erythropoietin binds to receptors on bone marrow cells, stimulating the production of red blood cells.
Paracrine Signaling
Paracrine signaling occurs when a cell secretes a signaling molecule that binds to receptors on nearby cells. This type of signaling is often used to coordinate the activities of cells within a tissue. For example, the neurotransmitter acetylcholine is secreted by nerve cells and binds to receptors on muscle cells, causing the muscles to contract.
Endocrine Signaling
Endocrine signaling occurs when a cell secretes a signaling molecule that travels through the bloodstream to reach target cells in distant parts of the body. This type of signaling is often used to regulate the activities of cells throughout the body.
For example, the hormone insulin is secreted by the pancreas and travels through the bloodstream to reach cells in the liver, muscle, and fat tissue, where it stimulates the uptake of glucose from the blood.
Each type of cell communication has its own advantages and disadvantages. Autocrine signaling is the most efficient type of signaling because it does not require the involvement of other cells. However, it is also the most limited type of signaling because it can only affect the cell that secretes the signaling molecule.
Paracrine signaling is more versatile than autocrine signaling because it can affect nearby cells. However, it is also less efficient than autocrine signaling because the signaling molecule must diffuse through the extracellular space to reach its target cells. Endocrine signaling is the most versatile type of signaling because it can affect cells throughout the body.
However, it is also the least efficient type of signaling because the signaling molecule must travel through the bloodstream to reach its target cells.
Cell Signaling Pathways: Ap Bio Cell Communication Quiz
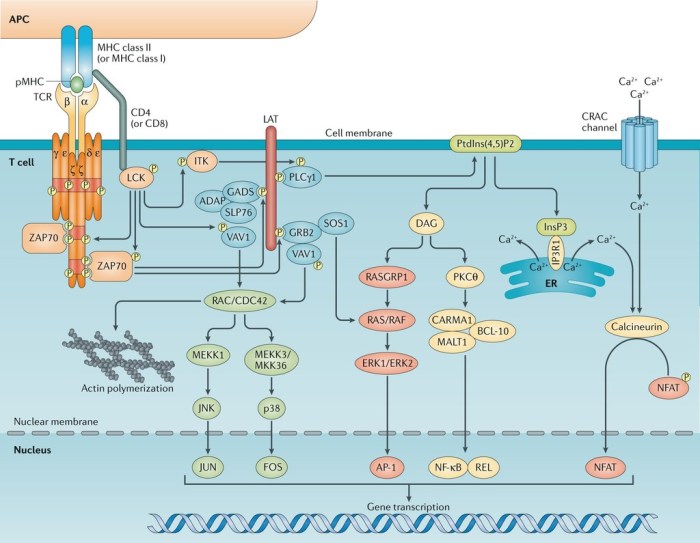
Cell signaling pathways are the routes by which cells communicate with each other and respond to external stimuli. They involve a series of molecular interactions that transmit signals from the cell surface to the nucleus, where they can trigger specific cellular responses.
Cell signaling pathways can be classified into three main types: ligand-gated ion channels, G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), and enzyme-linked receptors.
Ligand-gated Ion Channels
Ligand-gated ion channels are transmembrane proteins that form pores in the cell membrane. When a ligand binds to the extracellular domain of the channel, it causes a conformational change that opens the pore, allowing ions to flow into or out of the cell.
This change in ion concentration can trigger a variety of cellular responses, such as changes in membrane potential or the activation of other signaling pathways.
If you’re brushing up on AP Bio cell communication, don’t forget to check out the CLC 222 Module 4 exam answers . They can provide valuable insights into the key concepts covered in the AP Bio cell communication quiz. So, while you’re studying the intricacies of cell signaling, make sure to incorporate these resources to enhance your understanding.
G Protein-coupled Receptors, Ap bio cell communication quiz
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) are transmembrane proteins that are coupled to G proteins, which are heterotrimeric proteins that consist of three subunits: alpha, beta, and gamma. When a ligand binds to the extracellular domain of a GPCR, it causes a conformational change that activates the G protein.
The activated G protein then dissociates from the GPCR and interacts with other proteins in the cell, such as adenylyl cyclase or phospholipase C, to trigger a variety of cellular responses.
Enzyme-linked Receptors
Enzyme-linked receptors are transmembrane proteins that have an enzymatic activity on their cytoplasmic domain. When a ligand binds to the extracellular domain of an enzyme-linked receptor, it causes a conformational change that activates the enzyme. The activated enzyme then phosphorylates other proteins in the cell, triggering a variety of cellular responses.
Cell Communication in Health and Disease
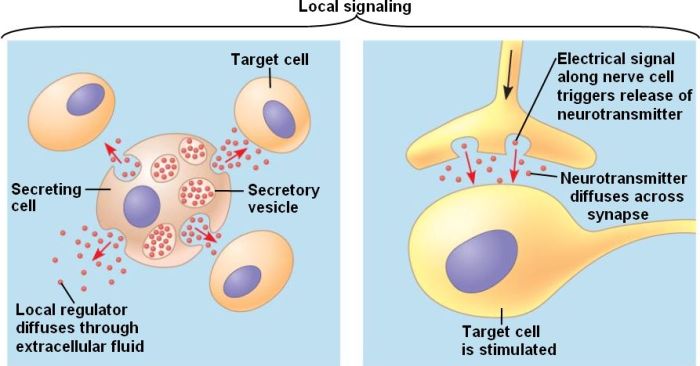
Cell communication plays a vital role in maintaining the delicate balance of homeostasis within the body. By constantly exchanging signals and coordinating their actions, cells ensure that all physiological processes function harmoniously.
However, when cell communication is disrupted, it can lead to a cascade of events that ultimately result in disease. This disruption can occur due to various factors, including genetic mutations, environmental toxins, and pathogens.
Diseases Caused by Disruptions in Cell Communication
- Cancer:Dysregulated cell communication is a hallmark of cancer. Cancer cells often exhibit defects in their signaling pathways, leading to uncontrolled cell growth and proliferation.
- Autoimmune diseases:In autoimmune diseases, the immune system mistakenly attacks the body’s own cells. This disruption in cell communication can be caused by faulty signaling molecules or receptors.
- Neurological disorders:Many neurological disorders, such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases, are characterized by impaired cell communication within the brain and nervous system.
- Infectious diseases:Pathogens often exploit cell communication pathways to gain entry into cells and manipulate their host’s immune response.
Applications of Cell Communication Research
Cell communication research has a wide range of applications in medicine, particularly in understanding and treating diseases. By studying how cells communicate, scientists can gain insights into the mechanisms underlying disease processes and develop new therapies that target these pathways.
One important application of cell communication research is in the development of drugs that modulate cell signaling pathways. For example, drugs that inhibit the growth factor receptors involved in cancer cell proliferation have been developed and used successfully to treat certain types of cancer.
Potential Benefits of Cell Communication Research for Treating Diseases
Cell communication research has the potential to lead to the development of new treatments for a wide range of diseases. By understanding how cells communicate, scientists can identify new targets for drug development and design therapies that are more effective and have fewer side effects.
Some specific examples of how cell communication research has led to new treatments for diseases include:
- The development of drugs that inhibit the growth factor receptors involved in cancer cell proliferation, which has led to new treatments for certain types of cancer.
- The development of drugs that target the immune system to treat autoimmune diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis and multiple sclerosis.
- The development of drugs that target the inflammatory response to treat diseases such as asthma and Crohn’s disease.
FAQ
What are the main types of cell communication?
Paracrine, endocrine, autocrine, and juxtacrine.
How does a cell receive a signal from another cell?
Through receptors on its surface or within the cell.
What is the role of cell communication in maintaining homeostasis?
It helps cells coordinate their activities and respond to changes in the environment.