Are clouds biotic or abiotic? This question has intrigued scientists and casual observers alike. As we gaze up at the sky, these celestial formations appear both ethereal and enigmatic. Are they merely collections of water droplets or do they harbor life within their billowing forms? Let’s embark on a journey to unravel the truth behind the biotic or abiotic nature of clouds.
Clouds are fascinating natural phenomena that play a crucial role in the Earth’s climate and weather patterns. They are composed primarily of water droplets or ice crystals suspended in the atmosphere. While clouds may appear to be alive due to their dynamic movements and ever-changing shapes, the scientific consensus is that they are classified as abiotic, meaning they are non-living entities.
Definition and Classification of Biotic and Abiotic Factors
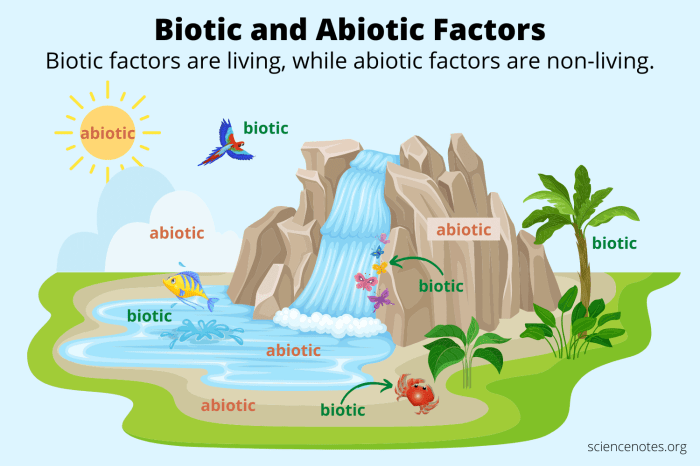
An ecosystem comprises two fundamental components: biotic and abiotic factors. Biotic factors encompass all living organisms, including plants, animals, fungi, and microorganisms, while abiotic factors refer to the non-living components of the environment that influence these organisms.
Examples of Biotic and Abiotic Factors
- Biotic Factors:
- Producers (plants)
- Consumers (animals)
- Decomposers (bacteria, fungi)
- Predators and prey
- Abiotic Factors:
- Sunlight
- Temperature
- Water
- Soil
- Atmosphere
Key Differences between Biotic and Abiotic Factors
- Origin:Biotic factors are living organisms, while abiotic factors are non-living components.
- Composition:Biotic factors consist of organic matter, while abiotic factors are composed of inorganic matter.
- Metabolism:Biotic factors exhibit metabolism, while abiotic factors do not.
- Reproduction:Biotic factors reproduce, while abiotic factors do not.
- Response to stimuli:Biotic factors respond to stimuli, while abiotic factors do not.
Characteristics of Clouds
Clouds are visible collections of water droplets or ice crystals suspended in the atmosphere. They form when warm, moist air rises and cools, causing water vapor to condense into tiny droplets or crystals.
Physical and Chemical Composition
Clouds primarily consist of water, either in liquid or solid form. Liquid water droplets are the most common component, forming the majority of clouds we see in the sky. In colder temperatures, water droplets can freeze into ice crystals, creating clouds with a crystalline structure.
In addition to water, clouds may also contain trace amounts of other substances, such as dust, pollen, and salt particles.
Types of Clouds
Clouds are classified into various types based on their appearance, altitude, and formation process. The main cloud types include:
-
-*Cirrus
Thin, wispy clouds composed of ice crystals, found at high altitudes.
-*Cumulus
Puffy, cotton-like clouds with flat bases, associated with fair weather.
-*Stratus
Flat, gray clouds that cover the entire sky, often leading to drizzle or light rain.
-*Nimbus
The question of whether clouds are biotic or abiotic remains a topic of scientific debate. Some argue that clouds are living organisms due to their ability to change shape and move. Others contend that clouds are simply collections of water droplets or ice crystals and are therefore non-living.
To better understand this topic, let’s consider an analogy. Imagine if a 3000kg car is pulled. The car moves, but does that make it a living organism? Similarly, while clouds exhibit certain behaviors, it doesn’t necessarily mean they are biotic.
Dark, rain-bearing clouds that produce precipitation.
-*Altostratus
Mid-level clouds that form a gray or blue-gray layer, often preceding rain or snow.
Role in the Earth’s Atmosphere
Clouds play a crucial role in the Earth’s atmosphere by:
-
-*Reflecting sunlight
Clouds reflect a significant portion of incoming solar radiation back into space, helping regulate Earth’s temperature.
-*Trapping heat
Clouds also act as a blanket, trapping heat radiated from the Earth’s surface, contributing to the greenhouse effect.
-*Producing precipitation
Clouds are essential for the water cycle, as they condense water vapor and release it as rain, snow, or other forms of precipitation.
-*Influencing weather patterns
Clouds can affect wind patterns, humidity, and temperature, influencing local and regional weather conditions.
Biotic and Abiotic Components of Clouds: Are Clouds Biotic Or Abiotic

Clouds are primarily composed of abiotic components, such as water vapor, ice crystals, and dust particles. However, there may be some potential biotic components present in clouds, albeit in very small quantities.
Bioaerosols
Bioaerosols are tiny particles that contain living or dead microorganisms, such as bacteria, fungi, and viruses. These particles can be transported through the atmosphere by wind and can become incorporated into clouds. While bioaerosols are not directly involved in cloud formation, they can potentially serve as cloud condensation or ice nuclei, influencing the formation of water droplets or ice crystals.
Absence or Minimal Presence of Biotic Components
Despite the potential presence of bioaerosols, the overall biotic component of clouds is generally considered to be minimal. This is because the harsh conditions within clouds, such as low temperatures, high levels of ultraviolet radiation, and the presence of antimicrobial substances, make it challenging for microorganisms to survive and thrive.
As a result, the biotic components of clouds are typically negligible and do not significantly contribute to cloud formation or precipitation processes.
Abiotic Factors Influencing Cloud Formation and Behavior
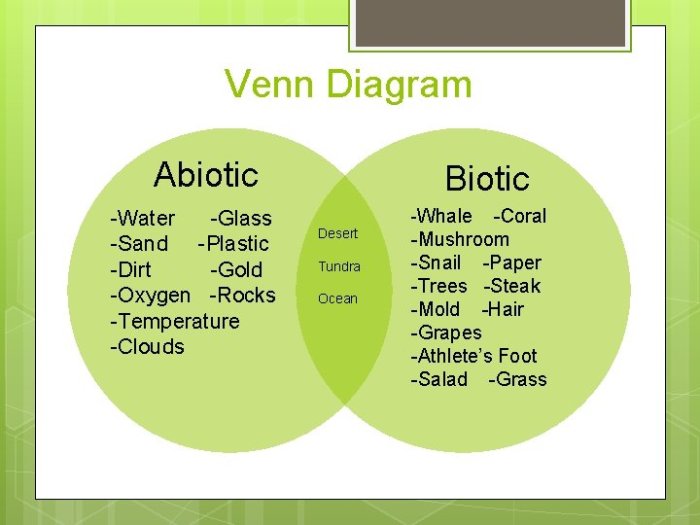
Cloud formation and behavior are significantly influenced by various abiotic factors, including temperature, humidity, air pressure, wind patterns, and topography. These factors determine the type, shape, and movement of clouds in the atmosphere.
Temperature
- Temperature plays a crucial role in cloud formation by influencing the amount of water vapor that can be held in the air.
- Warm air can hold more water vapor than cold air, so as air cools, it becomes saturated with water vapor and forms clouds.
Humidity
- Humidity refers to the amount of water vapor present in the air.
- High humidity levels promote cloud formation, while low humidity levels inhibit it.
Air Pressure
- Air pressure affects cloud formation by influencing the lifting and condensation of air.
- Low air pressure creates conditions that allow air to rise, cool, and condense, leading to cloud formation.
Wind Patterns
- Wind patterns influence the movement and shape of clouds.
- Winds can transport clouds over long distances and affect their shape by shearing and stretching them.
Topography
- Topography refers to the physical features of the Earth’s surface, such as mountains and valleys.
- Topography can influence cloud formation by creating updrafts and downdrafts, which can lead to the formation of clouds or precipitation.
Significance of Cloud Classification

Cloud classification plays a crucial role in weather forecasting, climate modeling, and research. By understanding the types of clouds present in the sky, meteorologists can make more accurate predictions about upcoming weather conditions and patterns.
Cloud Classification in Weather Forecasting, Are clouds biotic or abiotic
Cloud types can provide valuable information about atmospheric conditions and potential precipitation. For instance, cirrus clouds, composed of ice crystals, often indicate fair weather. In contrast, cumulonimbus clouds, towering and anvil-shaped, are associated with thunderstorms and heavy rainfall.
Cloud Classification in Climate Modeling
Cloud classification is essential in climate modeling as clouds significantly impact Earth’s energy balance and climate system. Different cloud types have varying radiative properties, affecting the amount of solar radiation reflected back to space and absorbed by the Earth’s surface.
FAQ Resource
Are there any living organisms in clouds?
While clouds themselves are abiotic, they can carry microorganisms, such as bacteria and fungi, that are transported by wind and precipitation.
Can clouds reproduce?
No, clouds do not possess the ability to reproduce or create offspring.
Do clouds have a lifespan?
Yes, clouds have a lifespan that can range from a few minutes to several hours or even days, depending on atmospheric conditions.